1. Related Terminology of Prcision Step Gauge Anyi-Step
1).Working surface
The exposed working surfaces of gauge blocks of step gauge
2).Origin working surface
The working surface used as the indication Zero of step gauge, usually marked “0”.
3).Measuring Range
Each working surface center to the center of Origin working surface.
4).Parellelism
The parellilism between each working surface and the Origin working surface. Figure 2, the biggest measured value from the 4 points which are 2mm away from the working surface center to the Origin working surface is the parellelism between this working surface and the Origin working surface.
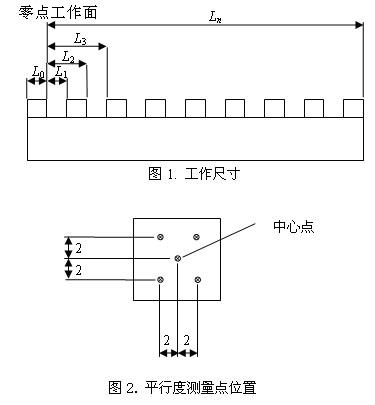
Fig.2 Points for measuring parallelism
2. Specifications
| Measuring range (R) (mm) |
Grade 1 |
Grade 0 |
Grade 00 |
Limit error
(μm) |
Parallellism
(μm) |
Limit error
(μm) |
Parallellism
(μm) |
Limit error
(μm) |
Parallellism
(μm) |
| 0<R≤300 |
±1.2 |
1.0 |
±0.8 |
0.8 |
- |
- |
| 300<R≤600 |
±1.8 |
1.5 |
±1.0 |
1.0 |
- |
- |
| 600<R≤1000 |
±2.5 |
1.5 |
±1.5 |
1.0 |
±1.0 |
1.0 |
| 1000<R≤1500 |
±4.0 |
2.0 |
±2.5 |
1.5 |
±1.5 |
1.5 |
1). Measuring Range
Measuring range in the table above, for example, ( 300<R≤600 ) means the measuring range is longer than 300mm, but shorter than 600mm. Its limit error and parallelism should be qualified with the measuring range. Meanwhile, its limit error and parallelism also should be qualified with its measuring range ( 0<R≤300 ). For example, a 600mm step gauge of Grade 0, its limit error is ±1.2μm within 300mm and ±1.8μm above 300mm. For other measuring ranges, just deduce like the above.
2).Parallelism
a). Anyi-step can be used horizontally or vertically. In adition to the required parallelism of gauge blocks, the parallelism of step gauge is also important when it is used vertically: Namely the parallelism of the hypothetical plane that contacts the end face of Anyi-step and each working surface of Anyi-step. Simple understanding is that when Anyi-step stands vertically on the inspection surface plate, the parallelism of each working surface of Anyi-step and the inspection surface plate must meet the relevant need (the flatness of the plate can not be too poor). This parallelism is quite strict when calibrating height gauge with step gauge.
b). For parallelism, clients usually doubt: why is the permissible error for parallelism here so big, compared to gauge block ? In fact, step gauge isn't used in the way gauge block is used. In many occasions, gauge block needs to be lapped with the object being measured. Sometimes, the extended surface that is lapped with the object being measured is used. Thus the amount of change of gauge block is very strict. When using step gauge , only the center part of each working surface is used. No matter what kind of guide rails to be calibrated they are, the repositioning error of the stylus probe to the center of step gauge's working surface is very small.
So long as the parallelism meets the above requirement, step gauge can exclude additional more errors caused by parallelism.
c). Special Note: The classification of Anyi-step is different from that of gauge blocks.
|

